Introduction
The Sabre Saw, also known as a reciprocating saw, is an extremely versatile cutting tool widely used in DIY projects and professional worksites. It can effortlessly cut through various materials, including wood, metal, and plastic. However, different materials require different types of blades. Choosing the wrong blade can reduce cutting efficiency and cause excessive wear or damage to both the blade and the material.
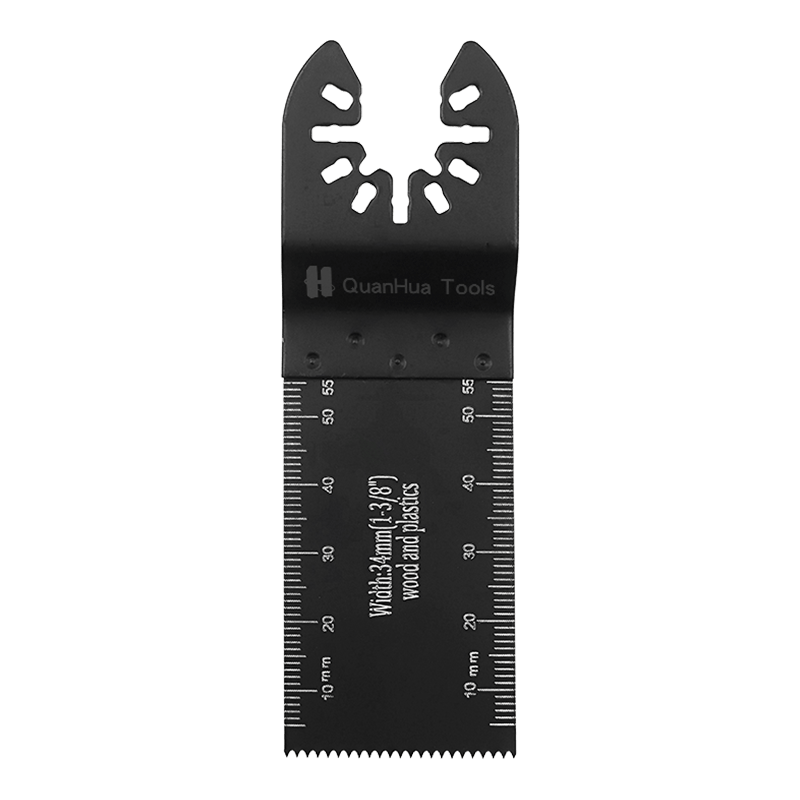
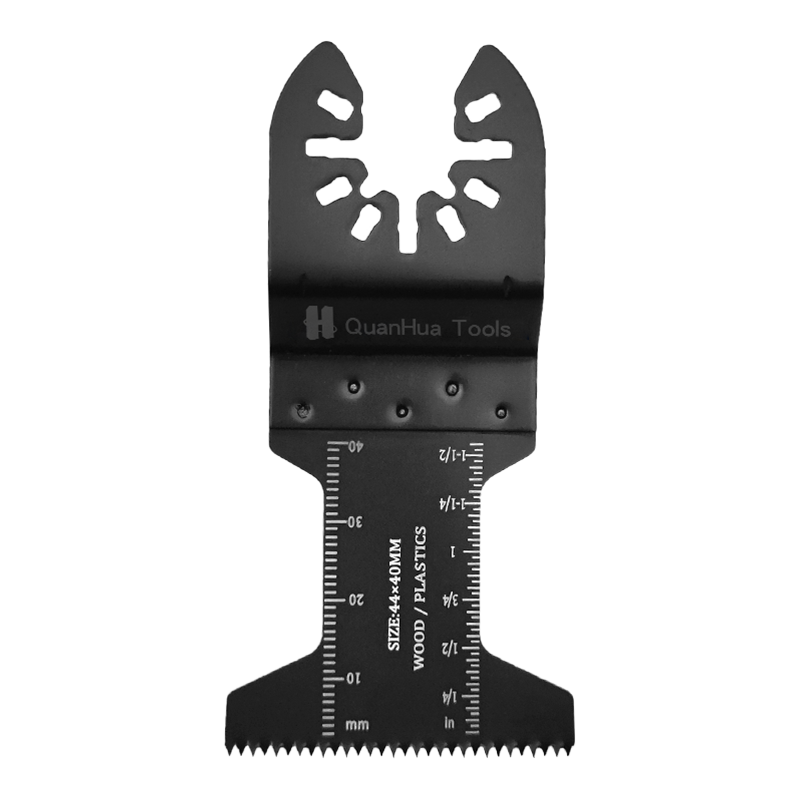
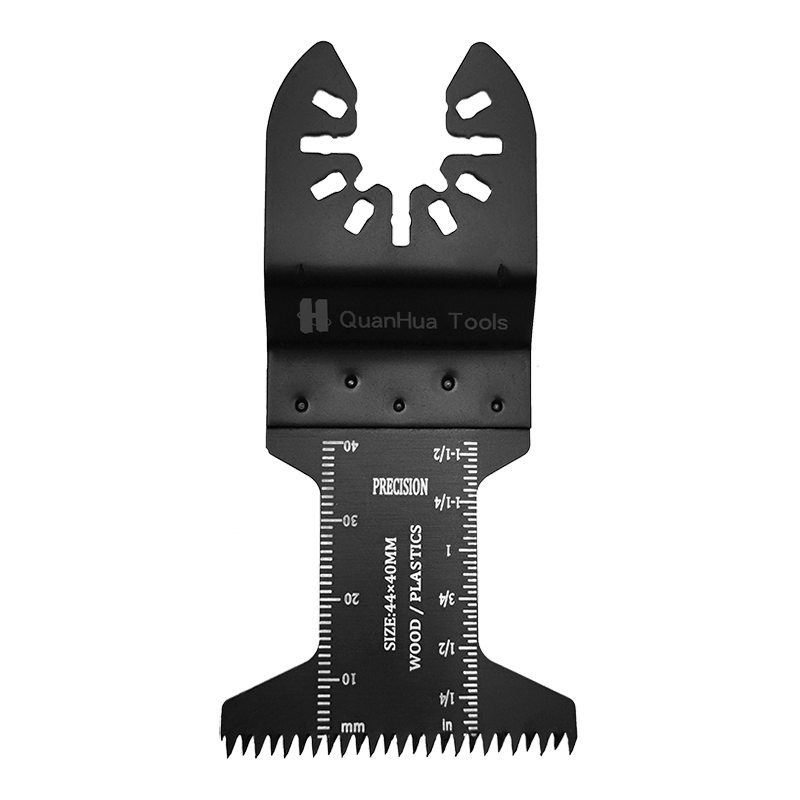
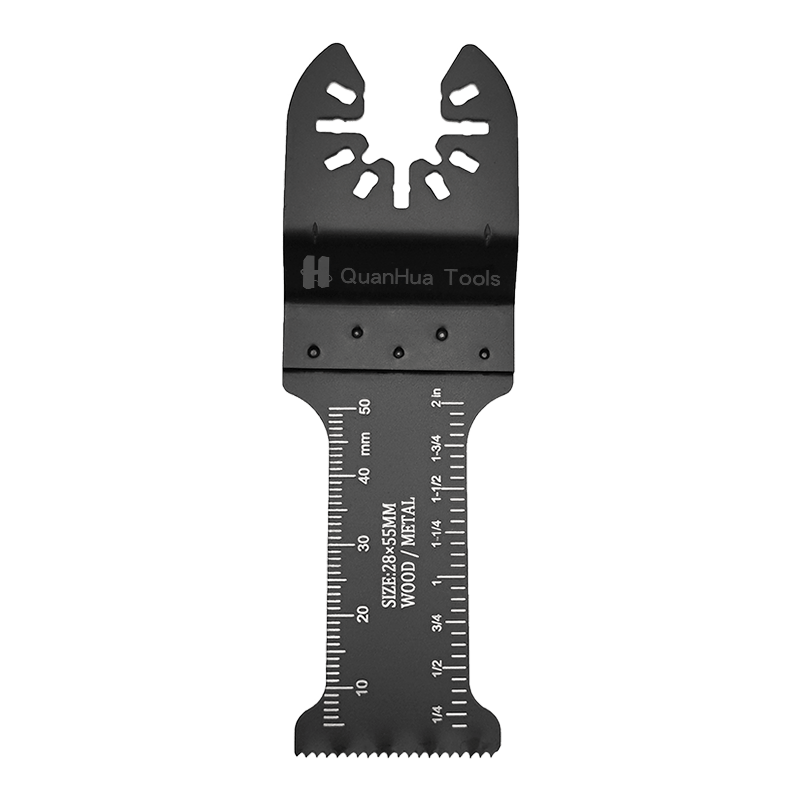
1. What is a Sabre Saw Blade
A Sabre Saw Blade is the core component of a reciprocating saw, typically mounted on electric or pneumatic saws. It performs cutting through rapid back-and-forth motion. Blades vary in tooth design, material, teeth per inch (TPI), and thickness to suit different materials and cutting needs.
Keywords: Sabre Saw Blade, reciprocating saw blade, cutting tool
2. Wood-Cutting Blade Features
Wood-cutting blades are typically made of high carbon steel or bi-metal. These materials keep the teeth sharp and withstand the stress of cutting wood. The TPI of wood-cutting blades is usually low, around 6-10, allowing faster cuts but producing a rougher cut edge.
Applications
- Wood boards, plywood, tree branches, softwood
- Plastic sheets or PVC pipes
- Light woodworking and DIY projects
Key Features
- Low TPI for fast cutting
- Durable and shock-resistant, suitable for rough cuts
- Affordable, ideal for home use
3. Metal-Cutting Blade Features
Metal-cutting blades are usually made of high-speed steel (HSS) or bi-metal, which are harder and capable of cutting through metal without dulling quickly. Metal blades have a higher TPI, generally 18-24, ensuring smooth and precise cuts while minimizing metal burrs.
Applications
- Steel pipes, aluminum, copper
- Thin metal sheets
- Precision metalworking and professional use
Key Features
- High TPI for smooth, precise cuts
- High hardness and wear resistance
- Longer lifespan despite higher cost
4. Key Differences Between Wood and Metal Cutting Blades
The main differences between wood and metal cutting blades are material, TPI, durability, and cutting speed. The table below summarizes these differences:
| Feature | Wood-Cutting Blade | Metal-Cutting Blade |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High carbon steel / Bi-metal | High-speed steel / Bi-metal |
| TPI | 6-10 (coarse) | 18-24 (fine) |
| Cutting Speed | Fast | Moderate, requires patience |
| Cut Quality | Rough | Smooth and precise |
| Suitable Materials | Wood, plastic | Metal sheets, pipes |
5. How to Choose a Sabre Saw Blade Based on Material
Selecting a blade depends on the material type, thickness, and cutting precision required:
Wood Cutting Recommendations
- Choose low TPI blades for faster cutting
- For thin wood sheets, medium TPI ensures cleaner cuts
- For hardwood, consider bi-metal blades for better durability
Metal Cutting Recommendations
- Choose high TPI blades for smooth cuts
- For thick metal sheets, use high-hardness bi-metal blades
- Monitor heat buildup to prevent blade damage
Mixed Material Use
If cutting both wood and metal, bi-metal multi-purpose blades are recommended, adjusting the cutting speed according to the material.
6. The Impact of TPI on Cutting Performance
Teeth per inch (TPI) is a key factor affecting cut quality and speed:
Low TPI
- 6-10 TPI, suitable for wood and soft materials
- Fast cutting speed but rougher cut edge
- Ideal for quick demolition or rough work
High TPI
- 18-24 TPI, suitable for metal and thin sheets
- Produces smooth, precise cuts
- Best for precision work and professional applications
7. Blade Selection Recommendations
When selecting blades, consider material type, TPI, hardness, and application:
- Wood blades: low TPI, fast cutting, suitable for rough or DIY projects
- Metal blades: high TPI, smooth cuts, suitable for precision metalworking
- Multi-purpose bi-metal blades: suitable for mixed materials, adjust speed accordingly
8. Tips for Use and Maintenance
Proper Installation
Ensure the blade is installed in the correct orientation and securely fastened to prevent shifting or detachment during cutting.
Cutting Tips
- Cut metal at lower speeds to avoid overheating
- Support wood properly to reduce vibration
- Wear safety gear such as gloves and goggles
Blade Maintenance
- Regularly check blade wear and replace dull or damaged blades
- Store blades in a dry environment to prevent rust
- Keep blades clean to maintain cutting performance